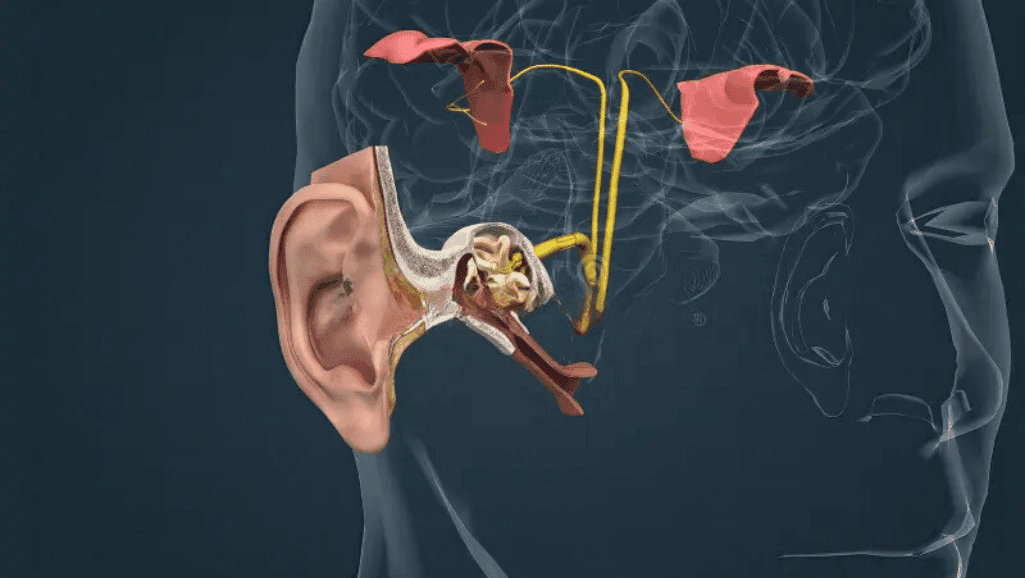
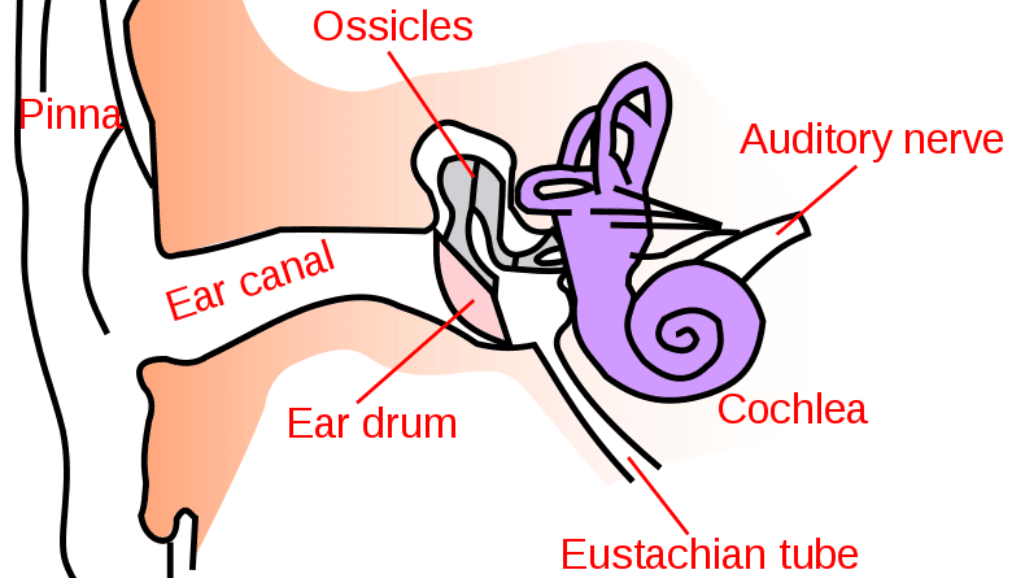
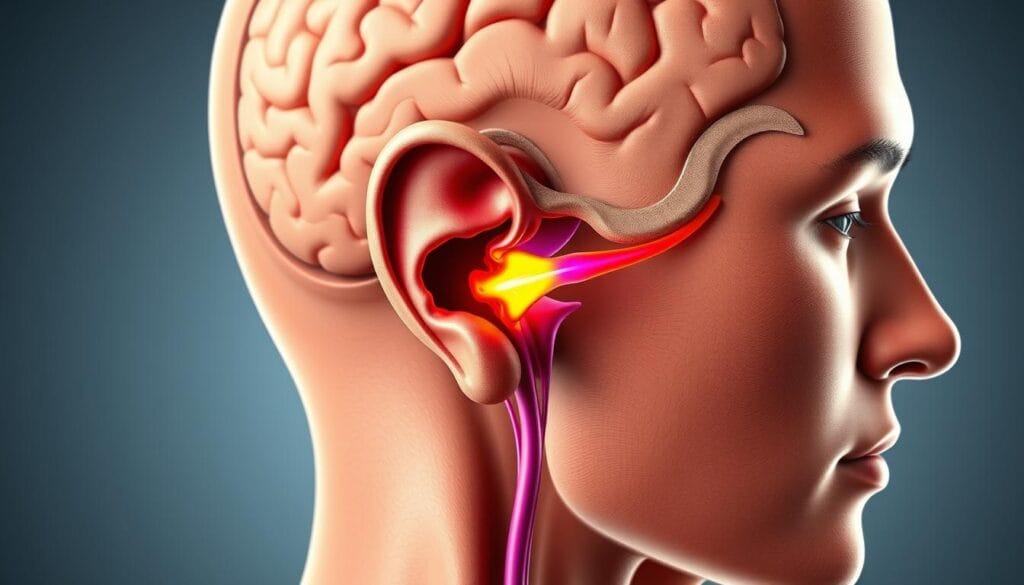
The journey of sound starts with the auditory nerve. It plays a key role in sending sound waves through the different parts of the ear. The health of the auditory nerve is crucial for hearing.
It works closely with auditory processing, hearing, and neural pathways. This teamwork is what makes us hear music or a quiet room. In today’s world, where sounds are often loud, it’s important to keep our auditory nerve healthy.
Key Takeaways
- The auditory nerve is pivotal for transmitting sound from the inner ear to the brain, influencing auditory processing.
- Neural pathways are integral for the conversion of sound vibrations into electrical impulses, vital for hearing function.
- Regular screening and management of ear health can mitigate the risk factors impacting auditory nerve health.
- Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the auditory system helps in maintaining optimal auditory nerve health.
- Professional guidance from hearing specialists is essential in cases of suspected auditory nerve issues.
Exploring the Function of the Auditory Nerve
The auditory nerve is key to our hearing. It turns sound waves into electrical signals sent to the brain. This process is vital for understanding speech and music.
Transmission of Sensory Information
Sound waves first hit the ear and become vibrations. These vibrations then go to the cochlea, where they become electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain, where we hear them.
Key Components in Hearing Mechanism
The auditory pathway transforms sound in several stages. The outer ear catches sound waves, which then go through the middle ear to the cochlea. Here, special cells send signals to the auditory nerve.
These signals then go to the brain for interpretation. Problems like auditory neuropathy show how crucial each part is. Early detection of issues is key for good hearing. For more on this, see hearing aids comparison analysis.
| Parameter | Description | Relevance to Auditory Nerve Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Pressure (daPa) | Measures the force of sound per unit area | Indirectly impacts how sound vibrations are perceived by the cochlea |
| Sound Intensity (dB) | Reflects the power per unit area of sound waves | Influences how nerve impulses are generated by sensory cells |
| Frequency (Hz) | Indicates the number of vibrations per second | Directly affects the rate of neurotransmitter release in the auditory pathway |
The entire system, from the ear to the brain, works together. It turns sound waves into audio signals we can understand. This complex process is vital for communication and connecting with our world.
The Complex Anatomy of the Auditory Nerve Pathway
The auditory nerve pathway is a complex network vital for hearing. It shows how the inner ear anatomy and the cochlea function work together. They turn sound waves into electrical signals our brains understand as sound.
Intricacies of Inner Ear Function
The inner ear anatomy is very specialized. It’s key for both hearing and balance. The cochlea, shaped like a spiral, is crucial for hearing. Inside, tiny hair cells change sound vibrations into electrical signals.
These signals go to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve. This shows how important the cochlea function is for hearing.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve and Hearing Function
The vestibulocochlear nerve, or cranial nerve VIII, has the cochlear nerve. It’s essential for auditory nerve function. It carries sound signals from the cochlea to the brain.
This complex process between the cochlea and the auditory nerve is key for clear sound perception and processing.
| Auditory Pathway Component | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Spiral Ganglion | Houses first-order neurons | Auditory Pathway |
| Cochlear Nerve | Transmits sound information | Ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei |
| Inferior Colliculus | Projects to thalamus | Brainstem |
| Medial Geniculate Body | Relays to auditory cortex | Thalamus |
| Primary Auditory Cortex (A1) | Processes auditory signals | Superior Temporal Gyrus |
The detailed connection in the auditory nerve function lets us hear sounds between 20-20,000 Hz. This shows how amazing the human hearing system is. The vestibulocochlear nerve helps us hear better and connect with our surroundings.
Common Auditory Disorders and Their Impact on Nerve Health
Auditory disorders like auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) affect hearing and the auditory nerve. This disorder lets sound into the ear but blocks it from reaching the brain. It makes it hard to understand speech and recognize sounds.
The impact of ANSD on the auditory nerve varies. This means different people need different treatments. Understanding this helps in managing their hearing health better.
Knowing how common ANSD is helps tailor treatments. It also sets realistic expectations for those affected:
| Condition | Incidence | Common Causes | Typical Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder | 1 to 3 per 10,000 births | Prematurity, jaundice, genetic mutations, exposure to ototoxic drugs | Varies from stability to worsening, with possible improvement |
| Genetic Influences | 25% risk with two carrier parents per pregnancy | More than 15 identified mutations (e.g., OTOF gene) | Depends on specific mutation, possible coexistence with other syndromic conditions |
| Associated Conditions | Varied | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Friedreich’s ataxia | Coexistence often complicates the hearing impairment |
| Treatment Approaches | Customized per individual | Hearing aids, cochlear implants, FM systems | Can range from ineffectual to highly beneficial for improved communication |
Hearing disorders like ANSD are tough on the auditory system and brain development, especially in kids. They can be diagnosed before birth or in newborns due to risks like premature birth and jaundice. This shows the need for careful monitoring and early help.
Early detection is key in managing these disorders. But, symptoms and outcomes can vary a lot, depending on the auditory nerve’s health.
Understanding auditory disorders helps us improve diagnosis and treatment. It also improves life quality by enhancing communication and using tools like sign language and speechreading.
Auditory Nerve Damage: Causes and Symptoms
It’s important to know the causes and symptoms of auditory nerve damage to help manage hearing health. Damage to the auditory nerve can cause sensorineural hearing loss. This makes it hard for people to hear sounds clearly.
Genetic Predispositions and Hearing Loss
Genetics can make some people more likely to have auditory nerve disorders. Some genes can mess up how the nerve sends sound signals to the brain. This can lead to hearing loss from birth or later in life. Early detection and treatment are key.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Nerve Damage
Being around loud noises for a long time can harm the auditory nerve. This includes sounds from machines, music, or even everyday loud places. It can cause sensorineural hearing loss that might be preventable with ear protection and avoiding loud sounds.
Some injuries, illnesses, or medicines can also hurt the auditory nerve. Knowing these risks helps us take steps to protect our hearing.
| Factor | Impact on Auditory Nerve | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Loud Noise Exposure | Damage to hair cells and auditory nerve fibers | Possibility of permanent hearing loss |
| Aging (Presbycusis) | Natural degeneration of auditory structures | Increased difficulty in understanding speech |
| Genetic Syndromes | Inherited malfunction of auditory mechanisms | Developmental delays in speech and language |
| Head Injuries | Physical trauma to auditory nerve or pathways | Acute, potentially irreversible hearing loss |
| Infections (e.g., Meningitis) | Inflammation and damage to nerve tissues | Temporary or permanent hearing reduction |
The Diagnostic Process for Auditory Nerve Health
Checking the health of the auditory nerve is key to fixing hearing problems and stopping them from getting worse. This process looks at how well the nerve and inner ear work together. It’s all about making sure the sound pathway is clear.
Role of Auditory Brainstem Response Tests
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) tests are very important. They check how the brain reacts to sound. Electrodes on the scalp record brain waves as sounds are played.
This helps doctors see if the auditory nerve is working right. An abnormal ABR can show problems, even if the outer hair cells are okay. This means the nerve pathway might be the issue.
Otoacoustic Emissions: Understanding Outer Hair Cell Function
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) tests check the outer hair cells in the cochlea. A probe sends sounds into the ear and measures the echoes. If echoes are present, it means the outer hair cells are working.
OAE tests are great for spotting cochlear problems early. They help make sure the cochlea is working well.
Using ABR and OAE tests together gives a full picture of hearing. New technology makes these tests even better. This helps doctors understand the auditory nerve’s health more accurately.
Modern imaging like MRI and CT scans also help. They check for things like tumors or bone problems that can affect hearing. Along with other tests, this makes diagnosis very thorough.
This detailed approach checks both the outer and inner parts of the ear. It helps doctors find the best treatments. This way, people with hearing problems can get better and live better lives.
Understanding Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder
Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) is a unique hearing problem. It affects the nerve fibers that carry sound to the brain. Even though the ear can pick up sounds, it can’t send them to the brain well. This makes it hard to understand speech perception abilities and hear well.
This condition can happen at any age, but it’s often found in newborns and young children. Things like being born early, severe jaundice, and genetic issues can increase the risk. ANSD’s effects can vary a lot, from mild hearing loss to being very deaf.
To diagnose ANSD, doctors use tests like the auditory brainstem response (ABR) and otoacoustic emissions (OAE). These tests check if the inner ear can detect sound and if the nerve can send it to the brain.
Treatment for auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder depends on the person. They might use hearing aids, cochlear implants, or FM systems. Speech therapy is also key, especially for kids, to help with speaking and communication.
For kids with ANSD, special education and visual aids like sign language are important. Using both sound and sight helps them learn and communicate better.
Even though ANSD is tough, research keeps getting better. This gives hope for a better life for those with ANSD. It’s important for doctors and families to work together to find the best treatment plans.
Advancements in Auditory Nerve Regeneration Research
In recent years, neurotology has made big strides in auditory nerve regeneration. This is thanks to new methods like gene therapy and advanced cochlear implants. These technologies help us understand hearing problems better. They also lead to treatments that could fix hearing loss.
Emerging Treatments and Gene Therapy
Gene therapy for hearing issues has made a big jump forward. Scientists have found and studied Otoferlin. They found that Otoferlin gene mutations cause a type of deafness.
This research could lead to new ways to fix hearing problems. It shows promise for auditory nerve regeneration that could fix genetic hearing loss.
Experimental Approaches in Neurotology
Studies in neurotology use zebrafish to learn about Otoferlin. This helps scientists understand how it affects hearing. It also helps in making new treatments for hereditary hearing loss.
Also, cochlear implants are getting better thanks to neurotology research. They aim to work more like our natural hearing.
Here are some stats to show why these treatments are needed:
| Condition | Prevalence | Potential Benefit from Gene Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| DFNB9 deafness | Significant in certain populations | High |
| Auditory neuropathy | Varies, commonly associated with OTOF mutations | Moderate to High |
| General hearing impairment | 360 million people worldwide (WHO, 2013) | Depends on the cause |
This table shows how important gene therapy and cochlear implant upgrades are. They could help treat many hearing problems. By fixing the genes behind hearing loss, like OTOF, researchers aim to improve life for millions.
The work on auditory nerve regeneration is exciting. It could lead to treatments that not only manage but also cure hearing loss. This is a big step towards understanding and treating hearing system disorders.
Importance of Early Detection in Auditory Nerve Health
The importance of early detection in hearing health is huge. Finding hearing problems early is crucial. It helps stop hearing loss from getting worse and allows for quick action. This is very important for kids, as it helps them learn and talk better.
Early detection of hearing loss in kids is very important for their growth. If not caught early, it can slow down their speech and language skills. This can hurt their school work and how they interact with others. So, parents, caregivers, and doctors must watch for signs of hearing loss and teach about it.
| Diagnostic Test | Utility | Diagnostic Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Test | Detects cochlear function | N/A |
| Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test | Detects auditory nerve function | 92-98 for tumors >1.5 cm |
| Pure Tone Audiometry | Assesses degree of hearing loss | N/A |
Working together is key to better auditory nerve detection. Awareness campaigns and school programs are important. They help more kids get tested early, like with ABR tests, to check their hearing.
Keeping hearing health in mind requires everyone’s effort. With more education, watching closely, and acting fast, we can protect kids’ hearing. This way, we can lower the chance of hearing loss in kids.
Protecting Your Hearing: Prevention and Maintenance
Understanding how to protect your hearing is key to keeping your ears healthy. It’s important to take steps every day to prevent hearing loss. By being careful with your ears, you can avoid damage from the environment.
Everyday Practices for Hearing Conservation
Our daily habits can greatly affect our hearing. Loud noises, like those from lawnmowers, can harm our ears. To prevent damage, we can take simple steps:
- Use earplugs when it’s very loud, like at concerts or sports games.
- Keep the volume low on headphones to avoid loud sounds.
- Take breaks from loud places to give your ears a chance to rest.
These actions are crucial for protecting our hearing. They help prevent hearing loss, which is common in the U.S.
Managing Risk Factors for Optimal Auditory Nerve Function
Some health and lifestyle choices can harm our hearing. To keep our ears healthy, we need to manage these factors:
- Keep your heart healthy through exercise and a good diet. This helps your ears too.
- Don’t smoke or be around secondhand smoke to lower hearing loss risk.
- Check with your doctor about any medicines that might harm your hearing.
By taking care of these areas, we can improve our hearing health. This is important for keeping our hearing sharp over time.
Preventing hearing loss is possible with the right steps. By making these habits a part of our daily lives, we can protect our hearing. This is especially important for people of all ages.
The Role of Cochlear Implants and Hearing Aids
Cochlear implants and hearing aids are key in helping people with hearing loss. They use hearing technology to make sounds clearer, not just louder. This improves how people with hearing loss experience sound.
Tech Innovations in Hearing Assistance
New tech has made hearing aids and cochlear implants much better. Today’s devices are smarter and fit each person’s needs better. This has greatly improved life quality for many.
For example, modern cochlear implants help people understand speech and hear everyday sounds better. This is true even in noisy places.
Factors Determining the Suitability for Cochlear Implants
Choosing the right person for a cochlear implant is complex. It depends on how much hearing loss they have, their age, and the health of their inner ear. Medical studies show that it’s about more than just hearing loss.
It’s about how well someone can adjust after surgery. This is why a thorough check is needed before surgery.
| Criterion | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimum Age | 6 months |
| Hearing Loss Type | Severe to profound sensorineural |
| Candidate Evaluation | Audiometry and speech recognition tests |
| Post-Implant Support | Follow-up care with audiologists and otolaryngologists |
Most people with cochlear implants see big improvements in hearing within three to six months. But, it’s important to know about the rare risks of surgery. This includes infections or problems with facial nerves. This is why picking the right person for surgery and good care after it are so important.
For more tips on keeping your ears healthy and preventing hearing loss, check out this resource. It has great advice on how to protect your hearing every day.
Auditory Nerve
The auditory nerve, also known as the hearing nerve, is key in neural transmission and auditory processing. It’s vital for diagnosing and treating hearing problems. This nerve has Type I and Type II neurons, which carry sound signals to the brain.
Stimulating the auditory nerve is crucial for turning sound waves into signals the brain can understand. This process starts in the cochlea and goes through the brain, affecting how we hear.
| Part of Auditory Pathway | Function | Key Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Cochlear nerve fibers | Transmit auditory signals to the brain | Contralateral lateral lemniscus |
| Vestibular nerve | Relays motion and position information | Vestibular apparatus/ganglion |
| Thalamic medial geniculate nucleus | Further processes auditory signals | Primary auditory cortex within the temporal lobe |
| Vestibular nuclear complex | Processes balance and spatial orientation | Medial, lateral, superior, and inferior nuclei |
Understanding auditory nerve stimulation better could lead to new treatments for hearing loss. This includes using cochlear implants. It shows how important research and innovation are in this field.
Improving how we treat the auditory nerve is crucial. It affects many treatments for hearing problems. New ways to help the auditory nerve could greatly improve people’s lives.
Research and understanding the auditory nerve are key. They help create better treatments for hearing issues. This makes the auditory nerve a vital part of hearing health.
Conclusion
The importance of auditory nerve health is clear for good sensory information transmission. As people get older, their AN function gets weaker. This is shown in studies where older adults have smaller CAP N1 response amplitudes.
Noise exposure also affects AN function, but age is a bigger factor. This means we should focus more on keeping our hearing healthy as we age.
Looking into auditory nerve function shows how vulnerable it is to aging and noise. Animal studies give us clues about what happens when we lose hearing. The longer we are deaf, the more our auditory neurons suffer.
This highlights the need for quick action and new hearing loss treatments. Cochlear implants have changed lives for many with hearing problems.
Research, like studies on Dunkin-Hartley guinea pigs, helps us understand how to help the auditory nerve. It shows us how to improve treatments and protect our hearing. This research is key to finding new ways to help people with hearing loss.