An air bubble in ear can really hurt and make daily life hard. Often, it’s because the eustachian tube isn’t working right. This tube is key for draining fluid and keeping ear pressure balanced. If it’s blocked, like by a cold, you might feel ear congestion and look for ways to feel better.
People often try to find remedies for air bubble in ear and ways to ease ear pressure relief. They might swallow or yawn to help open the eustachian tubes. If these simple steps don’t work, they might use special tools like Otovent or EarPopper to help balance the pressure.
For those worried about ear pressure changes at high altitudes, like on planes, decongestants can help. They reduce swelling in the nose, making it easier for the eustachian tubes to open up.
Key Takeaways
- Unequal air pressure due to eustachian tube dysfunction can lead to an uncomfortable air bubble in the ear.
- Natural actions like yawning and swallowing are first-line maneuvers for ear pressure relief.
- Devices like Otovent and EarPopper can provide ear blockage relief when simple techniques fail.
- Pre-flight decongestants may prevent ear congestion when flying.
- Persistent issues may require professional ear discomfort treatment and further medical intervention.
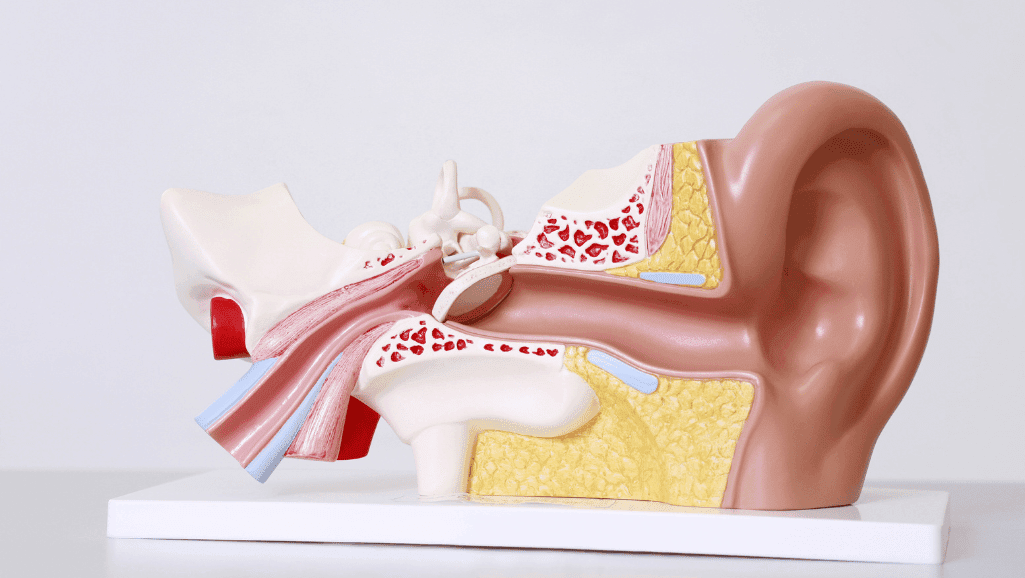
Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction and Ear Pressure Discomfort
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose. It helps keep air pressure balanced in the ears and drains fluids. Problems with this tube can cause inner ear discomfort and ear pressure discomfort. By learning about the causes of air in ear and managing eustachian tube dysfunction, people can find relief and avoid more issues.
The Role of the Eustachian Tube in Ear Health
The Eustachian tube is key to keeping middle ear pressure right and removing fluid in ear. It lets air pressure in the middle ear match the outside air pressure. This is important for the ear to work well and for good hearing. If it doesn’t work right, it can cause ear pain and hearing problems.
Common Causes of Blocked Eustachian Tubes
Blocked Eustachian tubes can happen for many reasons. These include allergies, colds, sinus infections, and some body shapes. This blockage can make ears feel full, hurt, and affect hearing.
- Allergies can make the Eustachian tube lining swell, making it less effective.
- Upper respiratory infections can swell and block the tube, making ear pressure worse.
- Too much loud noise can also cause problems, as studies show.
Symptoms Indicating Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction can be mild or severe. They can really affect how well you live. Signs include trouble with ear pressure, sharp pain, and inner ear discomfort. It’s important to notice these signs early to treat them well and avoid lasting damage.
- Feeling like your ears are plugged, especially when changing altitude, shows air pressure issues.
- Long-lasting ear pressure discomfort without a clear reason might mean fluid or blockage.
Here is a comparison of non-surgical and surgical interventions for ETD based on recent findings:
| Intervention | Description | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Non-surgical (Active observation) | Watching symptoms without immediate treatment to see if they go away on their own. | Varies |
| Small incisions in eardrum | Making small cuts to help drainage and pressure balance. | 1 to 3 days |
| Ear tube implantation | Putting small tubes in the ear to help air flow and fluid drainage. | Up to 18 months |
It’s important to understand eustachian tube dysfunction and middle ear pressure issues. By tackling the causes of air in ear and finding ways to remove fluid in ear, people can lessen ear pressure discomfort and improve their ear health.
Safely Relieving Pressure with Ear Equalization Techniques
Feeling uncomfortable due to air pressure changes is common. This happens when you fly, dive, or have colds or allergies. Using ear equalization techniques can help ease this pressure. It also prevents ear problems from air pressure changes.
To relieve blocked ear and keep the eustachian tube healthy, try the Valsalva, Toynbee, Frenzel techniques, and jaw exercises. These ear popping exercises help balance air pressure in the middle ear with the outside. This makes ear pressure more comfortable.
- The Valvasal maneuver: Pinch your nose closed and gently blow to force air back into your ear canal.
- Toynbee maneuver: Pinch your nose and swallow, which helps to open the eustachian tubes and balance ear pressure.
- Yawning or chewing: Regular jaw movements can help regulate pressure and are easy ear pressure home remedies.
- Frenzel technique: Using the tongue to push air into the throat while the nose is pinched closed.
Knowing how to handle blocked ear symptoms is crucial. Regular ear equalization is also important. Here are some facts that show why:
| Condition | Effect on Eustachian Tubes |
|---|---|
| Ear barotrauma (Airplane ear) | Can cause pronounced eardrum stress from air pressure differences. |
| Sinus infections | Leads to eustachian tube swelling and inner ear pressure. |
| Ear infections | Results in fluid buildup and subsequent pressure behind the eardrum. |
| Colds | Causes swelling and mucus, contributing to ear pressure. |
| Allergies | Inflames eustachian tubes, preventing pressure equalization. |
| Excessive earwax | Blocks the ear canal, causing ear stuffiness. |
| Foreign objects | Common in young children, leading to inner ear pressure. |
| Diving advice | Regularly practice ear clearing methods to prevent barotrauma. |
Using these ear popping remedies can make you feel better. It also helps you take care of your ears when you’re flying, diving, or have colds or allergies.
Common Remedies for Air Bubble in Ear
Dealing with air bubbles in the ears can be uncomfortable. There are many ways to find ear pressure relief and ear pain relief. You can try non-medicinal methods, over-the-counter solutions, or special devices to treat clogged ear treatment issues.
Non-Medicinal Maneuvers to Ease Ear Discomfort
Simple actions like chewing gum, yawning, or sucking on candy can help. These activities open the eustachian tubes, relieving pressure. The Valsalva maneuver, which involves gently blowing while pinching the nostrils closed, can also help equalize ear pressure.
Another method, the Frenzel maneuver, is great for divers. It clears the ears while keeping the mouth and nose closed.
OTC Solutions and When to Use Them
Over-the-counter (OTC) options like decongestant sprays or tablets can help before activities that worsen ear pressure. OTC nasal decongestants shrink mucus membranes, making it easier for air to flow. This can prevent ear discomfort during flights or diving.
Special Devices for Persistent Ear Blockage Problems
For those with frequent ear blockage, special devices can be very helpful. The Otovent and EarPopper allow users to manage ear pressure. Healthcare providers often recommend these for chronic ear pressure issues.
Knowing and using these options can greatly improve life for those with ear pressure and discomfort. Regular use of these methods before pressure changes can help prevent ear problems.
When to Seek Medical Treatment for Ear Discomfort Solutions
Many people face ear discomfort at some point. But, how long it lasts and how bad it gets is key. Home remedies can help, but some issues need a doctor’s help. Knowing when to see a doctor is important to avoid bigger problems like infections or hearing loss.
Ear pain remedies usually work for minor ear discomfort. For example, if a cold blocks your Eustachian tube. But, if your symptoms last longer than a cold or get worse, you should see a doctor.
Doctors might suggest topical nasal steroids for adults or ear tubes for kids with ear congestion. This is especially true if they keep getting ear infections. Even though chronic ear problems are rare, they need a doctor’s care to avoid lasting damage.
If medicines like decongestants and steroids don’t help, surgery might be needed. Doctors might do a procedure to open the Eustachian tube or put in ear tubes. They will decide if surgery is right based on how long and how bad your symptoms are.
Seeing a doctor is crucial if you have ear discomfort with severe symptoms like sharp pain, fluid, hearing loss, or fever. Prolonged symptoms can lead to bigger health issues. For more on hearing solutions, check out the benefits of invisible hearing aids for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Getting a doctor’s opinion is key to getting better. It helps fix both the symptoms and the cause, leading to full recovery.
Ear Barotrauma: Prevention and Treatment Options
Ear barotrauma is a common problem for people who face changes in air pressure. It can cause discomfort and even hearing loss. This issue is especially common among divers and frequent flyers due to pressure imbalances that stress the eardrum and middle ear structures.
It’s important to have good ear barotrauma treatment and prevention strategies. This is especially true for those who often deal with pressure changes. We will look into how to manage this condition and explore surgical options for chronic cases.
Identifying and Managing Ear Barotrauma
Knowing the symptoms of middle ear barotrauma is key to getting help quickly. Symptoms include ear fullness, discomfort, and sometimes hearing loss. These symptoms can get worse during altitude changes or underwater dives because of poor ear pressure equalization.
Managing this condition involves both self-help and medical treatments. Simple actions like yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum can help open the eustachian tube. This can equalize pressure inside the ear. For more structured ear sensations management, especially before flying or diving, nasal decongestants can be helpful. More information on self-care and treatment options can be found here.
Surgical Interventions for Chronic Ear Pressure and Discomfort
If non-invasive methods don’t work, surgery might be needed for ear barotrauma. Procedures like myringotomy, which involves making a small incision in the eardrum, can relieve pressure and drain fluids. Ventilation tubes can also be inserted to provide long-term relief and prevent further complications.
It’s crucial for patients to talk to healthcare professionals about their condition. They can assess the severity and discuss ear barotrauma treatment options. Each case is unique, so a personalized approach is often necessary.
In conclusion, taking care of your ears is key to preventing ear barotrauma. It also involves effective treatment strategies when symptoms occur. By being proactive about ear care, individuals can reduce discomfort and protect their hearing.
Conclusion
Exploring ear anatomy and understanding ear congestion is key to good ear health. Earwax buildup often causes temporary hearing loss, showing why cleaning ears regularly is crucial. Conditions like otitis media and Eustachian tube dysfunction can affect inner ear health, especially with colds or serious illnesses.
Ear discomfort during flights, known as ‘airplane ear’, and the quiet during train tunnels test our ear anatomy. These situations show how pressure changes can impact our ears.
Three out of four kids will get otitis media, with some cases lasting weeks. The American Academy of Otolaryngology suggests treatments like myringotomy and tubes to help. Using blocked ear remedies can help relieve pressure and pain.
Regular use of ear blockage remedies and knowing how to clear ear congestion is vital. These steps help prevent and manage blockages. For more serious cases, medical treatments can greatly improve outcomes and prevent long-term damage.
Access to new hearing aid technology and accessories also helps. Taking a proactive approach to inner ear health is essential. It keeps our ears healthy for everyday activities and challenges.