For those facing auditory neuropathy, finding the right treatment is key. This condition affects how sound reaches the brain. It’s important to get the right care for better hearing.
There are many ways to manage hearing loss now. This includes new treatments for different ages. It’s crucial to explore all options.
New treatments go beyond old hearing aids. Cochlear implants are now available. They show how far treatment has come.
Experts say a team effort is best. Audiologists, doctors, and therapists work together. They create a plan that fits each person’s needs.
Even with a good plan, some treatments are needed. Over-the-counter and prescription ear drops are used. But always get advice from a specialist for the best care.
Key Takeaways
- Identifying the right auditory neuropathy treatment is critical for managing the condition effectively.
- Ear drops for different ear conditions should be selected with care and preferably with medical advice.
- Cochlear implants may offer improved hearing for those with auditory neuropathy.
- Early diagnosis and intervention play a vital role in managing auditory neuropathy.
- Communication strategies, alongside technological aids, are part of a multidisciplinary treatment approach.
- Regular consultation with experts aids in the continual adaptation of treatment strategies.
Understanding Auditory Neuropathy and Its Impact
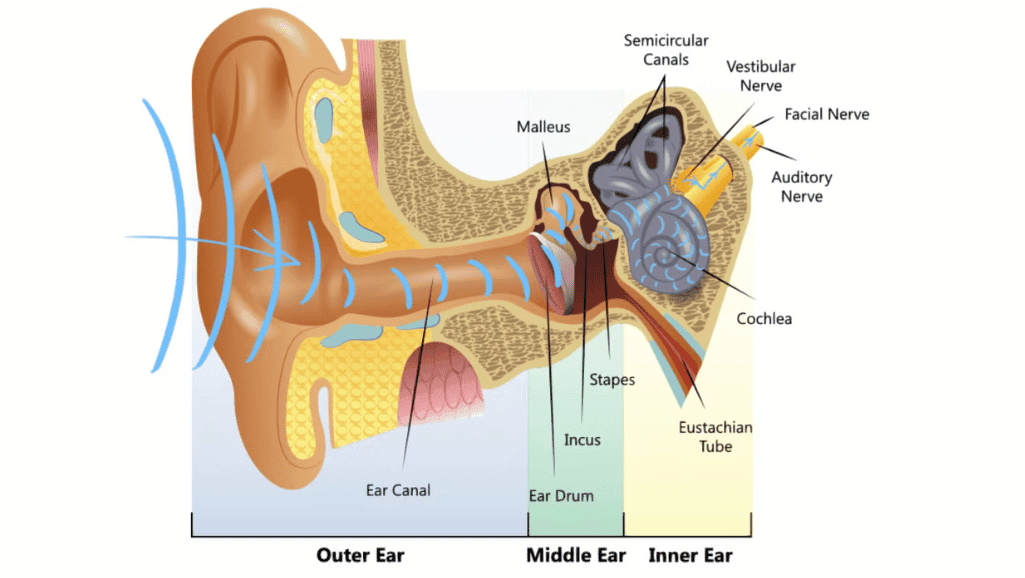
Auditory neuropathy is a complex condition that makes diagnosis and management tough. It affects how sound signals reach the brain. This leads to symptoms that make it hard to understand speech.
What is Auditory Neuropathy?
Auditory neuropathy happens when sound gets to the ear but signals to the brain are blocked. This can be due to damage to inner hair cells, the auditory nerve, or nerve signal disruptions. Symptoms include hearing sounds that fade in and out or speech that seems off.
How Auditory Neuropathy Affects Speech Perception
People with auditory neuropathy struggle to understand spoken words. This difficulty isn’t always linked to how severe their hearing loss is. Symptoms vary, making it hard to follow conversations or respond, affecting social and educational life.
The Challenge of Diagnosing Auditory Neuropathy
Diagnosing auditory neuropathy is tricky because symptoms vary and can look like other hearing problems. Tests like Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) and Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) are used. They check how the inner ear responds to sound and how signals get to the brain.
Getting an accurate diagnosis early is crucial. It helps manage the condition and improve quality of life.
It’s important to know how common this disorder is and why we need more awareness:
| Statistic | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence in Hearing Impairments | 1–10% of people with hearing impairments may have Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD). |
| Occurrence in Deaf Individuals | 10–15% of all individuals diagnosed as deaf may be affected by ANSD. |
| Development Age | Can occur in one or both ears and may develop at any age, with many cases identified at birth. |
| Language Acquisition Challenges | Children with ANSD often face difficulties in acquiring spoken language skills. |
| Diagnosis | Involves ABR, OAE, and other auditory function tests to determine the extent of the disorder. |
Exploring the Causes and Risk Factors of Auditory Neuropathy
It’s important to know the causes of auditory neuropathy and its auditory neuropathy risk factors. This is especially true for kids. The condition happens when the ear picks up sounds but can’t send them to the brain well.
Auditory neuropathy in children is linked to several high-risk conditions. Genetic problems, certain neurological disorders, and things that happen during and after pregnancy play a big role.
- Lack of oxygen during birth and severe jaundice in the neonatal stage are particularly critical risk factors.
- Exposure to infectious diseases like mumps and certain medication types also heightens the risk.
- Moreover, premature birth statistics correlate strongly with heightened risks of auditory neuropathy.
To better understand these factors, here’s a table:
| Condition | Related Risk Factor |
|---|---|
| Genetic Disorders | Inherited mutations affecting auditory signal transmission |
| Birth-related Issues | Lack of oxygen at birth, Premature birth |
| Postnatal Issues | Severe neonatal jaundice |
| Neurological Disorders | Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome, Friedreich’s Ataxia |
| Infectious Diseases | Mumps and related complications |
For more information on ANSD, visit the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center site. It offers detailed resources on this topic. Early diagnosis and treatment are key for kids with auditory neuropathy. They help improve developmental outcomes and quality of life.
Comprehensive Diagnosis of Auditory Neuropathy
Diagnosing auditory neuropathy needs a detailed approach. This ensures accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. Healthcare providers use tests like Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) and Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) to find auditory neuropathy.
Auditory neuropathy testing is key. It helps tell it apart from other hearing problems. People with auditory neuropathy might have normal OAE readings but abnormal ABR responses. This shows outer hair cells work, but sound doesn’t reach the brain right.
The Role of ABR and OAE Testing in Diagnosis
ABR and OAE testing are vital for diagnosing auditory neuropathy. The Guidelines for the Identification and Management of Infants and Young Children with Auditory highlight their importance. These tests show how the ear responds to sound, helping confirm the diagnosis.
Assessing Speech-Perception Abilities
Testing how well someone hears speech is crucial. It involves detailed tests to see how they process sounds. This helps find the best auditory neuropathy interventions. These might include special hearing aids or implants, like those from Starkey.
The Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Spotting auditory neuropathy early is key. Early detection means quicker auditory neuropathy interventions. It helps develop the right treatment plans, often with the help of auditory neuropathy specialists.
Children especially benefit from early diagnosis and treatment. A thorough diagnostic process, with skilled auditory neuropathy specialists and tailored treatments, is vital. It confirms the diagnosis and helps create treatment plans that meet each person’s needs.
Auditory Neuropathy Treatment Options and Strategies
In the world of hearing health, many treatments help those with auditory neuropathy. These treatments aim to improve how people communicate. They use advanced devices and therapies to do so.
The Use of Hearing Aids and Personal Listening Devices
Hearing aids are key for many with auditory neuropathy. They make sounds louder, helping those who still have some hearing. Personal listening devices also help, as they can be adjusted for each person’s needs.
Experts suggest looking into financial aid to get these devices. This is especially true if cost is a problem.
Cochlear Implants: A Viable Solution?
Cochlear implants might be a game-changer for some with auditory neuropathy. Unlike hearing aids, they don’t just make sounds louder. They send signals directly to the auditory nerve.
This can greatly improve how well someone hears in noisy places. But, each person’s situation is different. A careful check is needed to see if cochlear implants are right for them.
Educational and Communication Skills Development
Speech therapy is vital for those with auditory neuropathy, especially kids. It helps with speaking, reading, and social skills. For some, sign language or cued speech might also be used.
Experts say a team approach is best. This includes audiologists, speech therapists, and educators. They work together to support each person fully.
The treatment for auditory neuropathy combines technology and therapy. As technology and therapy improve, so do the chances for better outcomes. This gives hope to those dealing with this tough hearing disorder.
Conclusion
Our exploration of auditory neuropathy care has shown that treatment must be complex. Nearly 70% of kids with deep hearing loss have symptoms of auditory neuropathy. This shows how common this disorder is.
Auditory neuropathy services offer hope. Cochlear implants have a 90% success rate, which is a big step forward in treating hearing loss.
The success of auditory rehabilitation depends on more than just hearing aids or implants. It also needs a full treatment for auditory processing disorder. Studies show that up to 80% of patients can see big improvements with the right treatment.
Genetics play a big role, too. For example, the Slovenian Roma have a 10% rate of this condition. This sparks talks about how genes and services interact.
Our search for the best ways to treat auditory neuropathy goes on. It’s fueled by new research and a focus on patient care. Advances in tech and genetics bring hope for better lives.
Early detection and custom treatment plans are key. Places like the Mayo Clinic and Columbia Otolaryngology are leading the way. They use the latest methods to improve hearing and communication.